Displaying 1 to 15 of 25 Publications
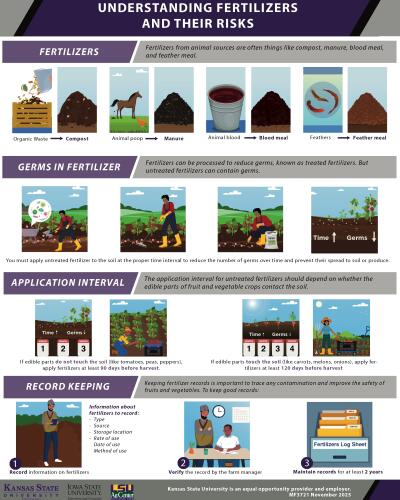
Understanding Fertilizers and Their Risks
by Sagar Pokhrel Katelynn Stull Manreet Bhullar
MF3721
This poster explains risks and best management practices related to using fertilizers from animal sources (such as compost, manure, blood meal, etc.). 11 x 17" color poster.
Published Date: Nov 2025
Environmental Considerations for Composting Livestock Mortalities
by Ron Graber Joel M. DeRouchey
MF2729
This publication addresses methods and considerations of composting livestock mortalities. 4 pages, b/w.
Revision Date: Feb 2024
How Much Gas Do Beef or Dairy Cattle Produce?
by Zifei Liu
MF3185
Beef and dairy cattle operations produce greenhouse gas emissions from feed digestion and manure decomposition. Producers need to be aware of what gases are emitted and why they are of concern so they can take steps to control and counteract these emissions. 4-page, color.Published Date: Apr 2015
Leachate from Silage and Wet Feed Storage
by Joseph P. Harner III et al.
MF3542
As responsible stewards of the environment, producers need to remain aware of the risk of leachate from silage and other wet feed ingredient storages, and take appropriate steps to reduce and manage the leachate/runoff from feed storage and processing areas. This publication describes factors for consideration and best practices to implement. 4 pages, color.Published Date: Oct 2020
Septic Tank Maintenance: A Key to Longer Septic System Life
MF947
For a septic tank to work effectively and to protect the rest of the wastewater system, it must be pumped (emptied) periodically. This bulletin describes pumping, frequency, and other procedures. 4-page.Revision Date: Aug 2010
Technologies for Odor Control in Swine Production Facilities
by Zifei Liu James P Murphy Joel M. DeRouchey
MF2918
Outlines best practices for managing odors and air pollution related to swine facilities. 6-page, b/w.Published Date: Apr 2014
Anaerobic Digestion of Livestock Manure: Feasibility and Factors to Consider
by Zifei Liu
MF3184
Anaerobic digestion (AD) of livestock manure offers a management option for livestock producers to generate energy from manure. Producers must weigh the costs of an AD system against the potential benefits. 4-page.Published Date: Mar 2015
Onsite Wastewater Treatment System Additives
by G. Morgan Powell DeAnn Presley
MF2877
Research indicates that additives are not a suitable alternative to proper septic tank maintenance. 2-page, b/w.Published Date: Feb 2009
Why Do Onsite Wastewater (Septic) Systems Fail?
by G. Morgan Powell Judith M. Willingham
MF946
Do your drains empty slowly? Does sewage back up? Do you have a wet, smelly spot in your yard? Is your septic tank effluent piped to a road ditch, etc? If so, your septic system is failing. 4-page.Revision Date: Sep 2010
Onsite Wastewater Systems - Overview
by G. Morgan Powell DeAnn Presley
MF2831
The simplest onsite systems are septic tank laterals and lagoon. The simplest septic systems have a septic tank and a dispersal field.Revision Date: Jul 2010
Get to Know Your Septic System
MF2179
If sewers & central wastewater treatment plants are not available, an onsite wastewater treatment system is needed. It must treat the wastewater and allow it to be absorbed by soil or evaporation.Revision Date: Aug 2010
Site and Soil Evaluation for Onsite Wastewater Systems
by Don Chisam G. Morgan Powell Judith M. Willingham
MF2645
A comprehensive site and soil evaluation is the key component affecting selection, design, and long-term performance of an onsite wastewater system.Published Date: Mar 2004
Grass Recycling
by Charles W. Marr Robert I. Neier
EP10
Up to 25 percent of your lawn’s fertilizer needs are supplied by clippings left on the lawn. Clippings do not contribute to thatch. Save time, money, landfill space by leaving clippings on lawn.Published Date: May 1995
National Air Quality Site Assessment Tool (NAQSAT) for Livestock Producers
by Zifei Liu
MF3367
Provides guidance to livestock producers and conservation planners on how to use NAQSAT, a NRCS (Natural Resources Conservation Service) approved educational website, to identify air quality concerns at livestock operations. 4 pages, b/w.Published Date: Jul 2017
Carbon Footprint of Livestock Production
by Zifei Liu
MF3180
Livestock producers can evaluate the carbon footprint of their production and make environmentally responsible choices. A number of factors influencing carbon emissions are discussed as well as ways to operate facilities efficiently and responsibly. 4-page, color.Published Date: Feb 2015
Displaying 1 to 15 of 25 Publications
 Sign in
Sign in